总体介绍
1
2
3
4
| public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V> {
}
|
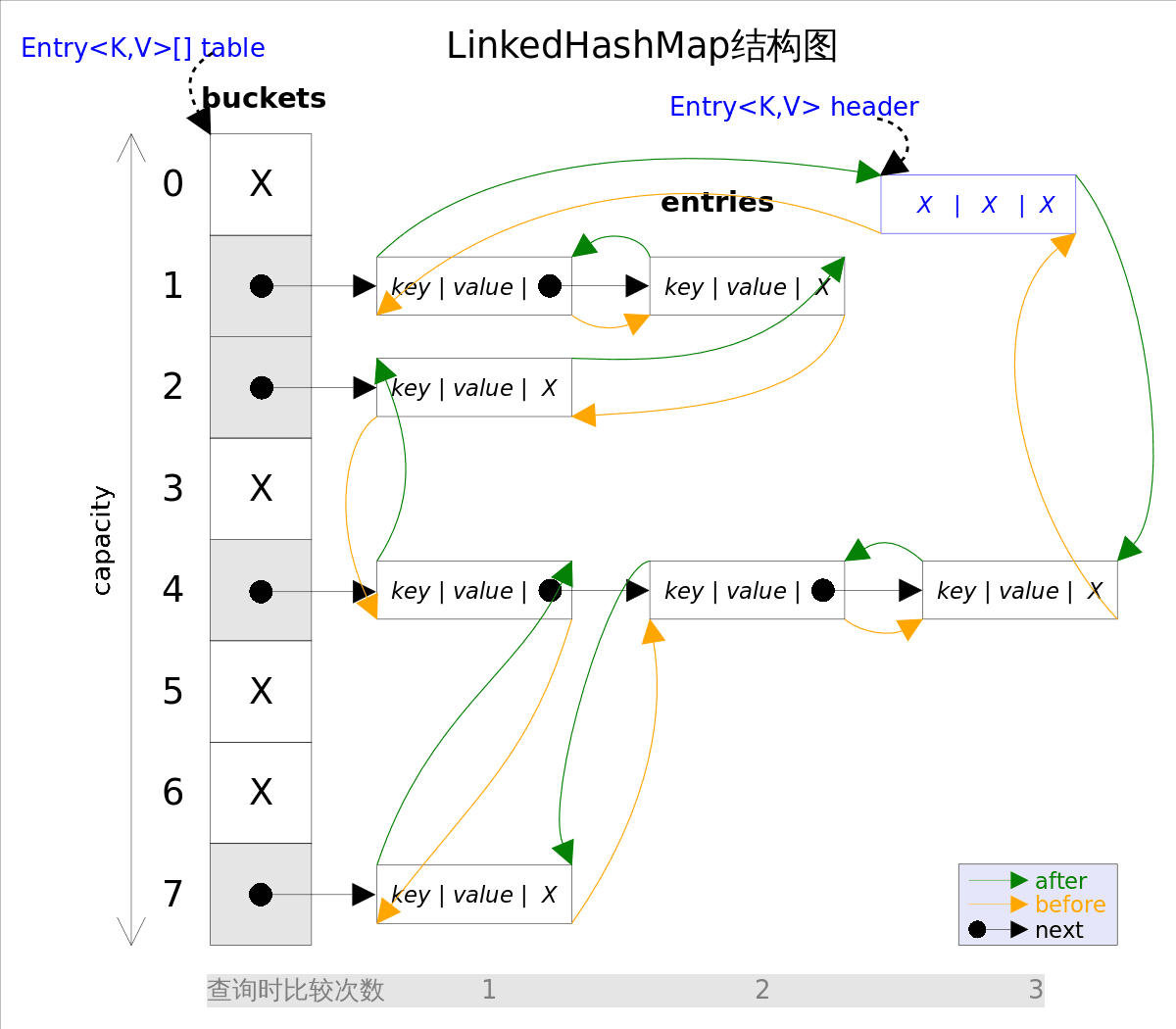
LinkedHashMap实现了Map接口,即允许放入key为null的元素,也允许插入value为null的元素。从名字上可以看出该容器是linked list和HashMap的混合体,也就是说它同时满足HashMap和linked list的某些特性。可将LinkedHashMap看作采用linked list增强的HashMap。
事实上LinkedHashMap是HashMap的直接子类,二者唯一的区别是LinkedHashMap在HashMap的基础上,采用双向链表(doubly-linked list)的形式将所有entry连接起来,这样是为保证元素的迭代顺序跟插入顺序相同。
方法剖析
get()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return defaultValue;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
|
Callbacks
1
2
3
4
|
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
|
afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
|
LinkedHashMap经典用法
LinkedHashMap除了可以保证迭代顺序外,还有一个非常有用的用法: 可以轻松实现一个采用了FIFO替换策略的缓存。
具体说来,LinkedHashMap有一个子类方法protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest),该方法的作用是告诉Map是否要删除“最老”的Entry,所谓最老就是当前Map中最早插入的Entry,如果该方法返回true,最老的那个元素就会被删除。
在每次插入新元素的之后LinkedHashMap会自动询问**removeEldestEntry()是否要删除最老的元素。这样只需要在子类中重载该方法,当元素个数超过一定数量时让removeEldestEntry()**返回true,就能够实现一个固定大小的FIFO策略的缓存。
示例代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
public class LRUCache_LinkedHashMap {
private int capacity;
private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache;
public LRUCache_LinkedHashMap(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
cache = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity, 0.75f, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return cache.size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
return cache.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache_LinkedHashMap lruCache = new LRUCache_LinkedHashMap(2);
lruCache.put(1, 1);
lruCache.put(2, 2);
System.out.println(lruCache.get(1));
lruCache.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(lruCache.get(2));
}
}
|
