Spring-IOC-实现原理详解-1-IOC初始化流程
前言
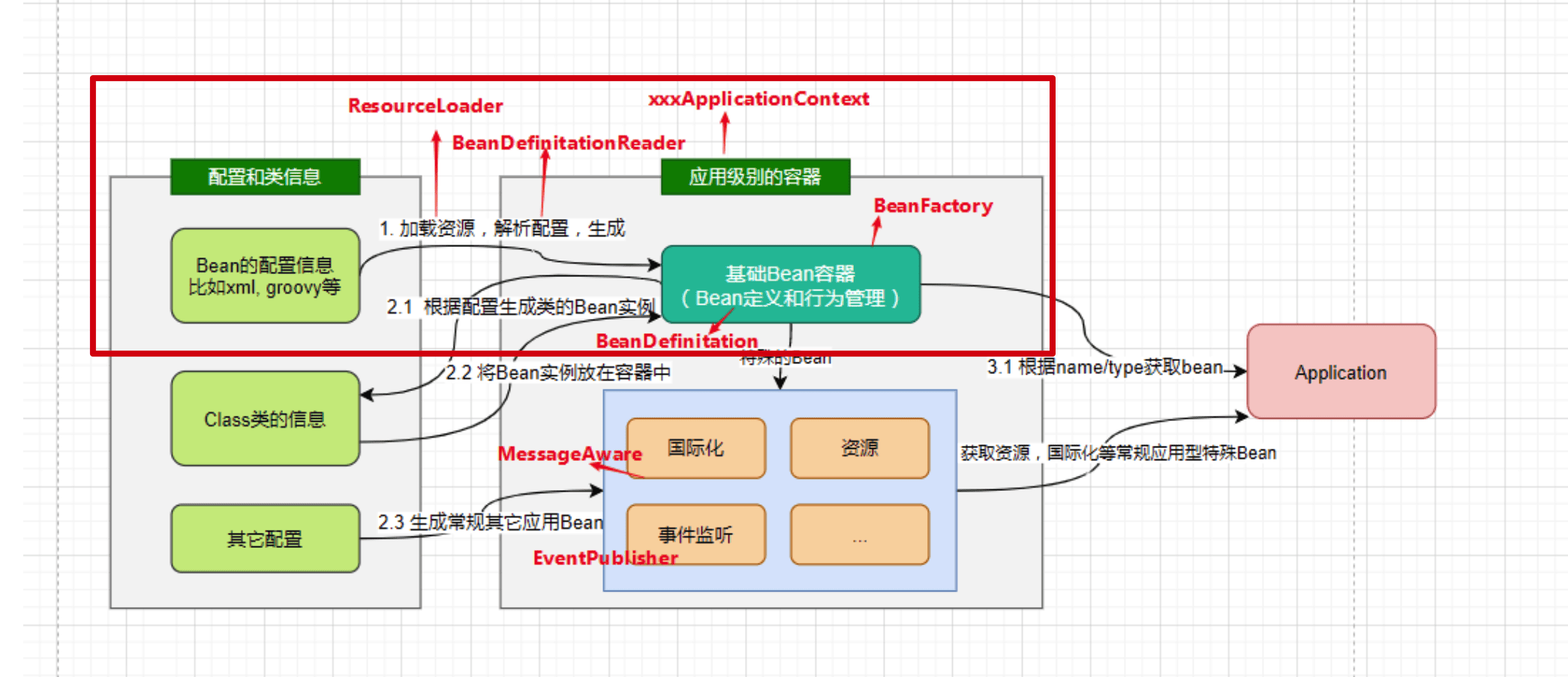
了解过了IOC的设计要点和设计结构,这篇来看一下源码的实现:Spring如何实现将资源配置通过加载、解析,生成BeanDefinition并注册到IoC容器中的(就是上图中圈出来的部分)。
如何将Bean从配置或注解中解析后放到IoC容器中的?
初始化的入口
SpringBoot
SpringBoot启动的话,当前applicationContext是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
xml方式
1 | // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造方法 |
注解方式
1 | // AnnotationConfigApplicationContext构造方法 |
初始化的主体流程 AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
Spring IoC容器对Bean定义资源的载入是从refresh()函数开始的。
refresh()是一个模板方法。
refresh()方法的作用是:在创建IoC容器前,如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器。
refresh的作用类似于对IoC容器的重启,在新建立好的容器中对容器进行初始化,对Bean定义资源进行载入。
1 | // AbstractApplicationContext#refresh() |
这里的设计上是一个非常典型的资源类加载处理型的思路,头脑中需要形成如下图的顶层思路(而不是只停留在流水式的方法上面):
- 模板方法设计模式,模板方法中使用典型的钩子方法
- 将具体的初始化加载方法插入到钩子方法之间
- 将初始化的阶段封装,用来记录当前初始化到什么阶段,常见的设计是xxxPhase/xxxStage
- 资源加载初始化有失败等处理,必然是try/catch/finally
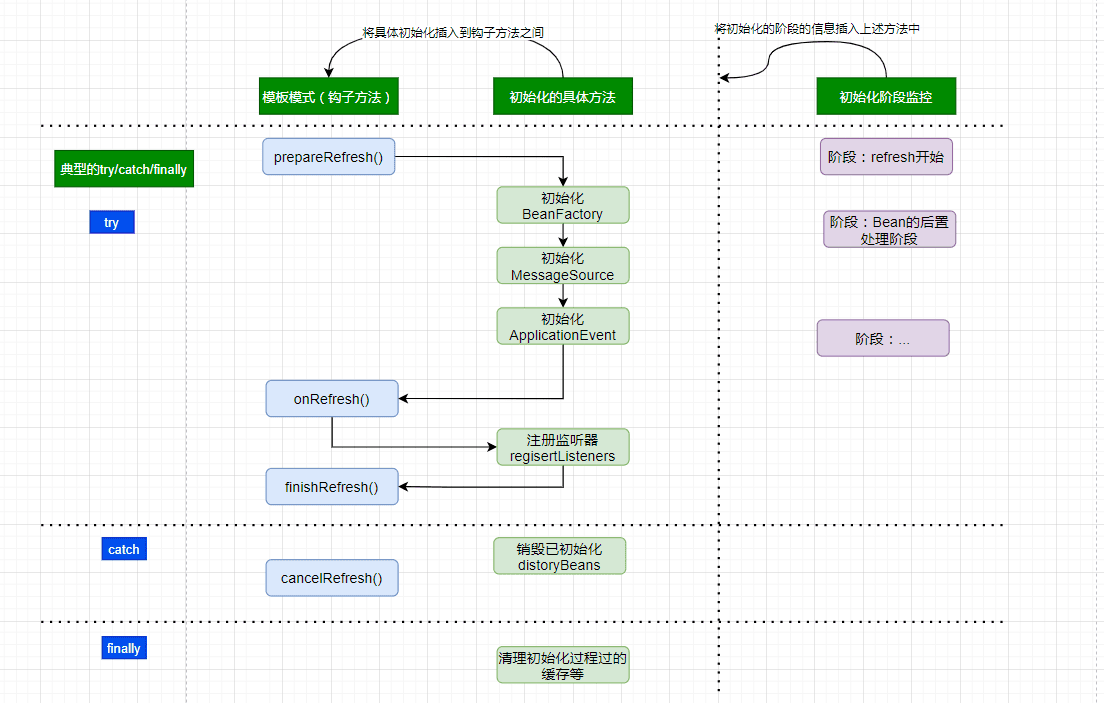
初始化BeanFactory之obtainFreshBeanFactory
AbstractApplicationContext的obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法调用子类容器的**refreshBeanFactory()**方法,启动容器载入Bean定义资源文件的过程,代码如下:
1 | // AbstractApplicationContext#ConfigurableListableBeanFactory |
refreshBeanFactory方法由以下两个子类实现:
- AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext类中只抽象定义了refreshBeanFactory()方法,容器真正调用的是其子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现的refreshBeanFactory()方法。
在创建IoC容器前,如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器。
方法的源码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29// public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext
// AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器
// 当前beanFactory为【private volatile DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory】;
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建DefaultListableBeanFactory,并调用loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)装载bean定义
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 对IoC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用载入Bean定义的方法,主要这里又使用了一个委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现调用子类容器
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}- loadBeanDefinitions
该方法由以下子类实现:

- loadBeanDefinitions
- GenericApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry
// GenericApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
/**
* Do nothing: We hold a single internal BeanFactory and rely on callers
* to register beans through our public methods (or the BeanFactory's).
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
*/
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}
初始化BeanFactory之loadBeanDefinitions
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,该方法由以下子类实现:
在各自的实现中,解析bean生成BeanDefinition。
解析过后的BeanDefinition在IoC容器中的注册
1 | // 通过BeanDefinitionRegistry将BeanDefinitionHolder注册到BeanFactory |
当调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils向IoC容器注册解析的BeanDefinition时,真正完成注册功能的是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
DefaultListableBeanFactory向IoC容器注册解析后的BeanDefinition
IOC容器本质上就是一个beanDefinitionMap, 注册就是将BeanDefinition put到beanDefinitionMap中。
至此,Bean定义资源文件中配置的Bean被解析过后,已经注册到IoC容器中,被容器管理起来,真正完成了IoC容器初始化所做的全部工作。
现在IoC容器中已经建立了整个Bean的配置信息,这些BeanDefinition信息已经可以使用,并且可以被检索,IoC容器的作用就是对这些注册的Bean定义信息进行处理和维护。
这些注册的Bean定义信息是IoC容器控制反转的基础,正是有了这些注册的数据,容器才可以进行依赖注入。